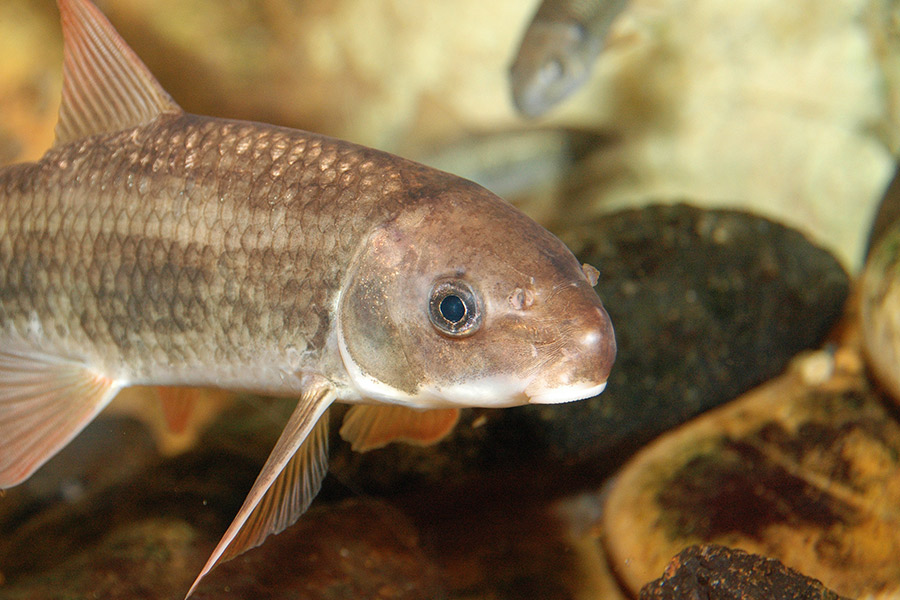
Habitat
Commonly found in pools with rock or silt substrate bottoms. These fish also prefer swift currents and runs of small to medium rivers, and are often present around fallen logs and debris.
Aquarium Location
Piedmont
Fun Facts
- The discovery of the robust redhorse in 1869 by Edward D. Cope was misinterpreted by fish biologists later on. Specimens of robust redhorse were mistakenly identified as smallfin redhorse.
- For over 100 years the redhorse went unrecognized, lost in the mistake made by scientists long ago. Between 1980 and 1992, however, large specimens of true robust redhorse were discovered in rivers of the Carolinas and Georgia.
- These latter fish were correctly identified.
- The habitat and life history of the species remains a mystery. The fish has been difficult to study because of the effort needed for sampling and their close relation to other species.
Diet
Robust redhorses eat small crustaceans, mollusks, insects, algae, and detritus (pieces of dead stuff).
Cool Adaptation
Like all fish declared suckers, the robust redhorse has a bottom facing mouth that is used to feed on bottom dwelling animals. This mouth is made up of two fleshy lips that are surrounded by finger-like projections called “papillae.” These lips allow this fish to create enough suction to remove algae from rocks and feed on crustaceans, mollusks, insects and detritus. These bottom feeding fish provide an important ecological service by “cleaning up” the bottoms of aquatic habitats of algae and dead materials. This service improves the overall health of habitats that are important for a variety of species.
Conservation Connection
Aside from being “lost” to science for 100 years, the robust redhorse has faced significant reduction in population due to habitat degradation. Agricultural, residential, and commercial development along robust redhorse habitat has lead to siltation of spawning grounds; stream alteration and channeling has caused a decline in robust redhorse habitat. In addition, the non-native blue and flathead catfish are known to predate on robust redhorses, which have a low number of individuals reaching sexual maturity. Lastly, dams and weirs block historic migration routes of reproducing fish. An inter-agency alliance called the Robust Redhorse Conservation Committee is working to restore habitat for this species, and replenish rivers where they were once abundant. What’s more, awareness of the specie’s decline has lead to research for determining life history, population dynamics, and genetics. Through education, RRCC and institutions such as the South Carolina Aquarium show the need for habitat protection and stronger conservation ethics.